Our pear trees are semi-dwarf, growing to 15’ high and wide. Plant pear trees in a sunny spot with well-drained, fertile soil that’s slightly acidic, with a pH of 6 to 7. Water regularly and feed established trees with Espoma Tree-tone in spring and summer.
CLICK HERE to check current availability and preorder fruit trees on our webstore.
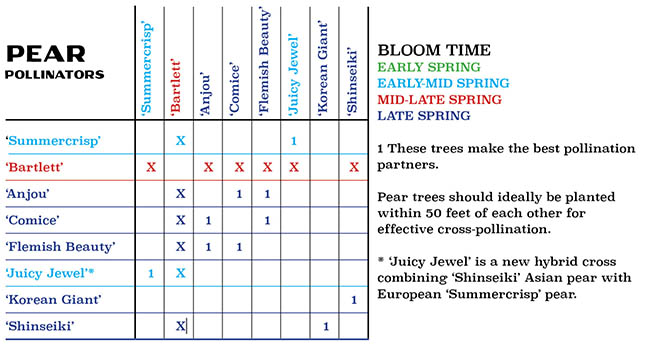
‘Bartlett’ is the best known pear. Medium-sized or larger fruits are ripe when they turn completely yellow and give off a sweet aroma. Self-fertile, but can be planted with ‘Summercrisp’ to boost fruit production.
‘Comice’ is a late season pear with yellow skin dotted with russet. Seet, tender and aromatic. Stores well. Plant with ‘Flemish Beauty’ or ‘Red Anjou’ to cross-pollinate. ‘Bartlett is also a reliable pollinator although it blooms slightly earlier.
Shape, flavor and texture of ‘Red Anjou’ is much like their green counterparts, but their rich maroon color sets this variety apart as a showy pear among pears in a fruit bowl or basket! Plant with ‘Comice’ or ‘Flemish Beauty’ to cross-pollinate. ‘Bartlett is also a reliable pollinator although it blooms slightly earlier.
‘Flemish Beauty’ is a hardy Belgian pear. A great choice for growers in cold climates, fruit is medium to large and rounded in shape with yellow skin that has a beautiful red blush. Excellent for fresh eating and drying. Plant with ‘Comice’ or ‘Red Anjou’ to cross-pollinate. ‘Bartlett is also a reliable pollinator although it blooms slightly earlier.
‘Summercrisp’ is an early-season pear that thrives in the upper midwest. Blooms in May with fruits reaching maturity in mid-August. Flesh is sweet, firm and crisp. Plant with ‘Bartlett’ for cross-pollination.
‘Juicy Jewel’ is a new early-to-mid season Asian pear with fruit blushed with orangey-pink. Unlike European pears, which ripen to a soft, creamy texture, Asian pears are known for their crisp, apple-like texture. This new ‘Shinseiki’ and ‘Summercrisp’ cross was developed at the University of Minnesota for cold hardiness and earlier fruit. Plant with ‘Bartlett’, ‘Korean Giant’
‘Korean Giant’ Asian pear produces very large globe-shaped golden, tan fruit. Pears are crisp, juicy and sweet. Plant with ‘Shinseiki’ to cross pollinate.
‘Shinseiki’ Asian pear produces round to oblong, smooth, sweet, and tender yellow fruit. Pollinators include ‘Bartlett’ and ‘Korean Giant’.
Espalier pears are grafted with cross-pollinating varieties and can be grown in smaller spaces or in formal landscape designs.
Semi-dwarf fruit trees grow 15’ high and wide.
PLANTING: Amend soil by mixing up to 50% compost with existing soil.. Plant tree so soil level in container is level or slightly higher than surrounding soil. Water in to remove air pockets around roots and mulch with wood chips. The first season, water regularly to establish tree.
FERTILIZING: Adequate nutrition is essential for quality fruit production. The best thing you can do is top-dress with compost every year. A general rule of thumb for adding additional fertilizer is to apply a combined 2/3 pound of bone meal and 1/3 Texas greensand to each tree the first year, double that the second year, and triple the third and subsequent years. Fertilizer should be broadcast on the soil surface around the drip line of the tree. The “drip line” is the circular line at the outer ends of the branches.
SCAFFOLD TRAINING: Improperly trained fruit trees have very upright branch angles which can result in excessive vigor and serious limb breakage under a heavy fruit load. Larger branches can be spread out using short wooden boards with a notch cut in each end to catch the branch. Hanging weights on branches or tying it down with string wrapped loosely around the limb are other useful methods for spreading branches. All upright growth from scaffold branches should be pulled down to a horizontal position or removed.
OPEN SCAFFOLD TRAINING: The open center system is good for peach and nectarine trees for maximum sunlight exposure, maximum yield, and best quality. Top the central leader and allow well-spaced side shoots to develop. Each year, remove diseased, broken, and low-hanging limbs and vigorous upright shoots that may have developed on the inside of the main scaffolds.
PRUNING: Pruning fruit trees during winter dormancy will invigorate the tree and cause it to grow and branch more the following season. Do dormant pruning in late winter or early spring after risk of severe freeze is over. Remove dead or diseased wood also. After tree resumes growth in the spring, continue to train the scaffold branches of the tree as you did the previous growing season. Prop lateral branches out to a 50 to 60 degree angle. Summer pruning will devigorate the tree and cause it to grow less in that growing season.
FRUIT THINNING: Ensure good fruit size and prevent tree breakage by thinning fruit. Approximately three to four weeks after bloom or when the largest fruit are as large as a quarter, fruits should be removed by hand so that the remaining fruits are spaced about every 8”.
POLLINATION: Self-pollinating, but production will increase when two or more varieties are planted together. All of the following trees are semi-dwarf, growing 12-15’ tall, 14’ wide.




